 |
|
|
AMT Nickel Alloy Powders
for Additive Manufacturing or 3D Printing |
 |
 |
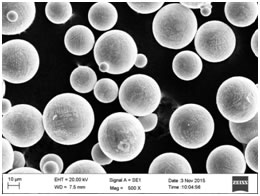
| AMT625-A |
3D Printing Parts By A fine Powders |
 |
 |
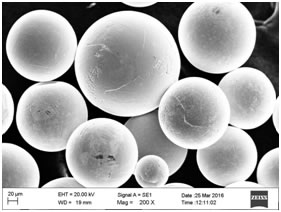
| AMT718-B |
3D Printing Parts By B Thick Powders |
1. Chemical and Physical Properties |
AMT
Type |
Weight Percent Max |
Ni |
Cr |
Mo |
Nb |
Mn |
Fe |
Si |
Cu |
Al |
Ti |
C |
AMT625 |
Bal |
20.0-23.0 |
8.0-10.0 |
3.15-4.15 |
≤0.5 |
≤5.0 |
≤0.5 |
≤0.5 |
≤0.4 |
≤0.4 |
≤0.1 |
AMT718 |
50.0-55.0 |
17.0-21.0 |
2.8-3.3 |
4.75-5.5 |
≤0.35 |
Bal |
≤0.35 |
≤0.3 |
0.2-0.8 |
0.65-1.15 |
≤0.08 |
|
AMT Nickel Alloy
Powders |
Powder Type |
Particle Size, µm |
Density, g/cm3 |
Flow velocity, s/50g |
Tap |
Apparent |
A Series |
15-53um |
≥5.0 |
≥4.0 |
- |
B Series |
53-150um |
≥5.5 |
≥4.2 |
≤20 |
|
| 2. Characteristics of AMT Nickel Alloy Powders
|
Our A series AMT Nickel alloy fine powders are highly spherical with low porosity. The oxygen and other contaminants are very low as well. In addition, the particle size distribution is tailorable. Nickel alloy fine powders have exceptional combination of high temperature strength, toughness, and resistance to degradation in corrosive or oxidizing environments.
Our B series AMT nickel alloy thick powders are highly spherical with an excellent flowability. The porosity is very low. The oxygen and other contaminants are very low as well. In addition, the particle size distribution is tailorable. AMT nickel alloy thick powders have excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance.
|
3. Applications of AMT Nickel Alloy Powders |
AMT nickel alloy fine powders have led to a wide and diversified range of successful applications in aircraft engine components, gas turbine and chemical processing structural. The A series AMT Nickel alloy fine powders are usually used in powder bed Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) which can make small and fine parts no need machining.
AMT nickel alloy thick powders are widely used in aircraft engine components, gas turbine and chemical processing structural. The B series AMT nickel alloy thick powders can be used in Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS) or Direct Metal Deposition (DMD). The alloy parts after such additive manufacturing are big and rough, usually need machining. |
| |
| |
|
 |
 |
 |
|

